Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
However, a company may have a provision on such shares that allows the shareholders or the issuer to force the issue. How valuable convertible common stocks are is based, ultimately, on how well the common stock performs. Most preference shares have a fixed dividend, while common stocks generally do not. Preferred stock shareholders also typically do not hold any voting rights, but common shareholders usually do. Preferred stock offers consistent and regular payments in the form of dividends, which resemble bond interest payments. Like bonds, shares of preferred stock are issued with a set face value, referred to as par value.
What Is «Stock Dividend Distributable»?
Preferred stocks offer more regular, scheduled dividend payments, which may be appealing to some investors, but they may not provide the same voting rights or as much potential for growth in value over time. Cumulative shares incentivize investors with the promise of a minimum return on investment. If preferred shares are cumulative, all past suspended payments must be made to preferred shareholders in full before common stockholders can receive anything at all. And if a company is unable to pay cumulative dividends by their due date, it may have to pay interest on future payments. A preferred stock is a class of stock that is granted certain rights that differ from common stock.
Consumer Products & Retail
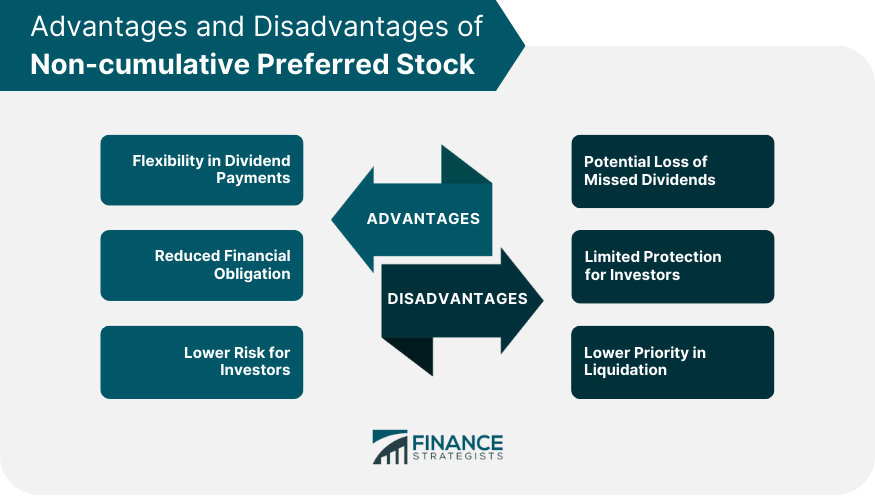
Cumulative shares require that any unpaid dividends must be paid to preferred shareholders before any dividends can be paid to common shareholders. Because preferred stocks’ par values are fixed and do not change, preferred stock dividend yields are more static and less variable than common stock dividend yields. You calculate a preferred stock’s dividend yield by dividing the annual dividend payment by the par value. It’s also worth noting that preferred stocks are callable in a way common stocks aren’t.
However, participating preferred stockholders may still be entitled to a dividend. These participating dividends may be tied to company achievements such as total sales, earnings, or specific margins. A participating preferred stockholder may also earn these types of dividends on top of what the company issues as “normal dividends,” assuming the company has enough finances to make all payments. However, preferred stock comes with the right to receive dividends prior to common stockholders and have a higher priority in getting paid back if the company goes bankrupt and is liquidated. Convertible CPS provides investors with the potential for capital appreciation in the company’s common stock while still receiving a fixed dividend rate.
The Difference Between Preferred & Ordinary Shares
- Stockholders are therefore entitled to that portion of the corporation’s assets and earnings.
- Cumulative preferred stock accumulates unpaid dividends and ensures their eventual payment, providing a measure of security to investors.
- In other words, this kind of stock is “preferred” over the common stock holder.
- CPS is typically issued by companies that need to raise capital but do not want to dilute the value of their common stock or do not qualify for traditional bank loans.
- With this type of stock, the issuing company has the right to call, or repurchase, the shares at a set price on a defined date.
- The terms of the preferred stock will be outlined in the company’s articles of association or incorporation.
Preferreds are issued with a fixed par value and pay dividends based on a percentage of that par, usually at a fixed rate. Just like bonds, which also make fixed payments, the market value of preferred shares is sensitive to changes in interest rates. However, the relative move of preferred yields is usually less dramatic than that of bonds. Cumulative preferred stock accumulates unpaid dividends and ensures their eventual payment, providing a measure of security to investors.
Preferred shareholders have priority over common stockholders when it comes to dividends, which generally yield more than common stock and can be paid monthly or quarterly. These dividends can be fixed or set in terms of a benchmark interest rate like the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR), and are often quoted as a percentage in the issuing description. There are a number of strong companies in stable industries that issue preferred stocks that pay dividends above investment-grade bonds.
The features of preferred stock provide investors with certain benefits, but also come with caveats that potential buyers need to be aware of. Below is an overview of how preferred stocks work, and how investors can decide if it’s the right fit for their portfolio. Because par values are not the same as trading values, you have to pay attention to the trading price of preferred shares as well.
Preference shares, also known as preferred shares, are a type of security that offers characteristics similar to both common shares and a fixed-income security. The holders of preference shares are typically given priority when it comes to any dividends that the company pays. In exchange, preference shares often do not enjoy the same level of voting rights or upside participation as common shares. Preferred stocks offer many of the most attractive features of common stocks and bonds, but they are not a single solution to all of your investment needs. They do not typically provide as much growth potential as growth stocks, which can raise the risk that you fall short of your savings goals if you allocate too much to them. As with stocks, dividends paid on preferreds may also not be guaranteed and like bonds, some preferreds can be taken away from you, or “called,” by their issuers.
While this provides flexibility to the company, it introduces an element of uncertainty for investors, as their investment could be redeemed earlier than expected. Convertible preferred stock adds another layer of flexibility to the investment. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links.
Convertible CPS is typically issued with a lower dividend rate than non-convertible CPS. CPS is typically issued by companies that need to raise capital but do not want to dilute the value of their common stock or do not qualify for traditional bank loans. Fidelity is not recommending or endorsing this investment by making it xero partner program available to its customers. If a company decides that it can’t pay a dividend, it can choose to skip paying that dividend. There are four kinds of preferred shares, all of which offer unique benefits to the holder. There is no optimal type — choosing the right kind means knowing which best suits the investor’s goals.


